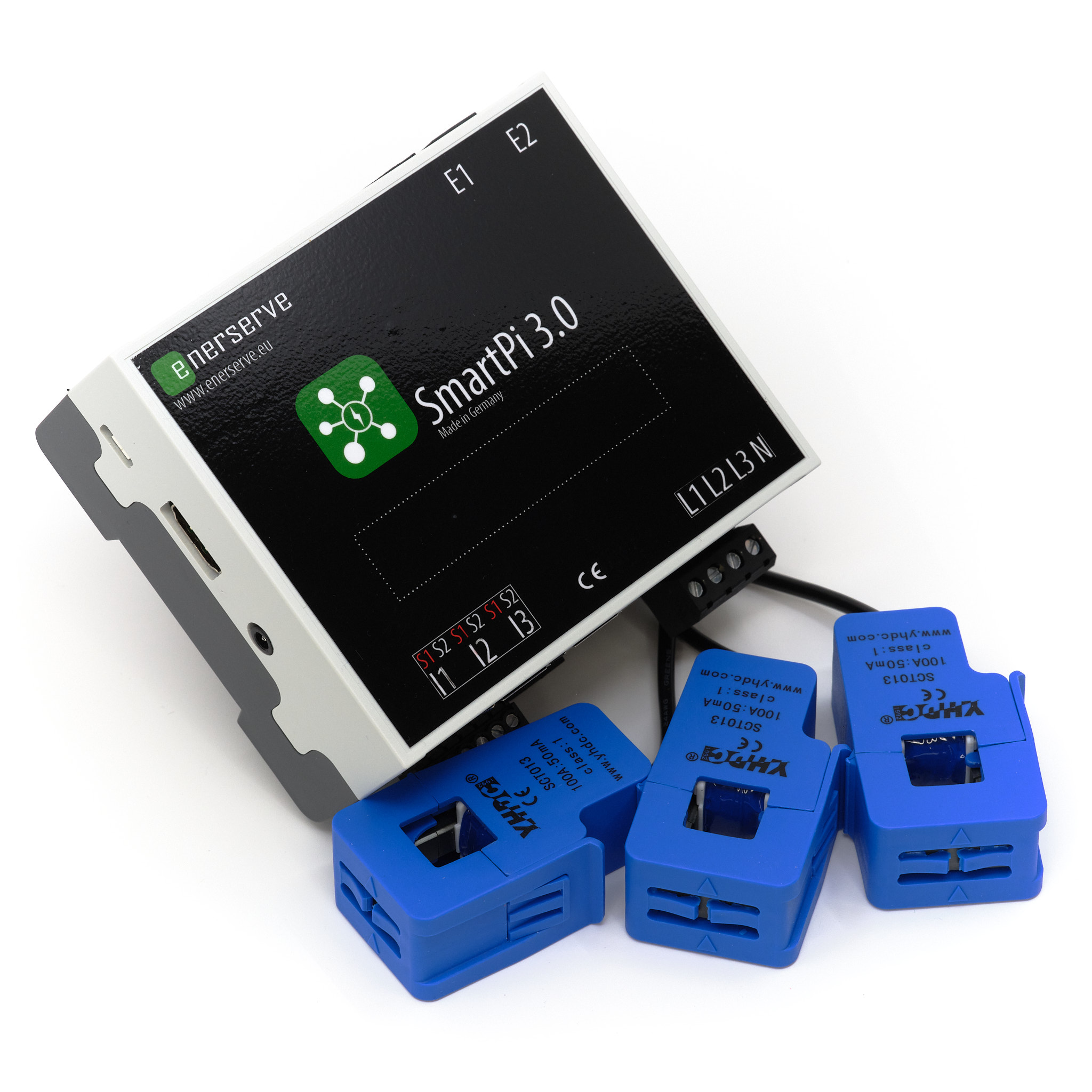

Das SmartPi 3.0 Erweiterungsmodul erweitert den Raspberry Pi
Mit dem SmartPi 3.0 können die Stromverbrauchsdaten bequem
Ströme
Spannungen
Leistungen
Wirkleistung
Blindleistung
Scheinleistung
Arbeit Bezug
Arbeit Einspeisung
Leistung Bezug
Leistung Einspeisung
Frequenz
Cos Phi
Der Strom wird beim SmartPi berührungslos über Kabelumbauwandler gemessen
Konnektivitätsprofi
Eigene Node-Red-Module ermöglichen die Integration in weitergehende Steuerungsabläufe
Der eingebaute Webserver des SmartPi stellt die Messdaten grafisch aufbearbeitet bequem per Browser oder Tablet / Smartphone zur Verfügung.
Eine Modbus-Schnittstelle (TCP) rundet das ganze Paket ab.
Open Source Smart Meter für den Raspberry Pi
Ideal, um den SmartPi in eigenen Projekten zu verwenden
Beispiele die mit dem SmartPi aufgebaut werden können:
- Energiemonitor über Netzwerk und Internet
- Netzfrequenzüberwachung
- Netzspannungsüberwachung
- Alarme bei Stromverbrauchern
- Alarme bei erhöhtem Verbrauch
- Integration in Energiemanagementsysteme
- Kostenüberwachung
Auf dem SmartPi 3.0 ist ein RTC (Real Time Clock) vorhanden, um den SmartPi 3.0 auch ohne Netzwerkverbindung zuverlässig betreiben zu können. Die Stromversorgung des gesamten Systems erfolgt über das integrierte Netzteil aus der Messspannung. Ein unzuverlässiges Hantieren mit Netzteilen an Micro-USB-Buchsen entfällt somit.
Sekündliches Auslesen von Strom, Spannung und Leistung
Sekündliches Auslesen vieler weiterer Daten
Minütliches speichern der Werte in der Datenbank
MQTT-Support
Prometheus-Support (noch nicht dokumentiert)
Node-Red Integration
Modbus-TCP
Modbus-RTU (über Erweiterungsmodul)
CSV-FTP-Upload
Weboberfläche zur Darstellung und Konfiguration
EMETER-Protokoll
LoRaWAN-Support (über Erweiterungsmodul)
Raspberry Pi kompatibler Verbinder
Raspberry Pi kompatible Größe
Galvanische Trennung
Integrierte Stromversorgung aus dem Spannungsmesspfad über stabile Klemmen (wahlweise 2A DC-Strom)
Opensource Treiber und API
Strommessung auf 3-Phasen
Anschluss für Kabelumbauwandler mit einem Sekundärausgang von 50mA, 333mV und 1A (optional 5A beim SmartPi 3.1)
Schraubklemmen zum Anschluss der Strom- und Spannungsmessung
Kompatibilität mit allen Raspberry Pi-Modellen
Gepufferter RTC (der Raspberry Pi läuft auch ohne Internetverbindung nach einem Stromausfall stabil weiter)
Wertiges Gehäuse mit Hutschienenbefestigung
Externer I2C-Anschluss über Modularbuchsen
Externer SPI-Anschluss über Modularbuchsen
Technische Daten
| SmartPi-Modul | SmartPi mit RaspberryPi | |
| Spannungsmessbereich | 0-230V eff. | |
|
3-phasig oder 3 x 1-phasig |
||
| Strombereich | abhängig von den Stromwandlern (0-100A mit den mitgelieferten Wandlern) | |
| 3-phasig (berührungslos mit Stromwandlern) | ||
| Messgenauigkeit | 2% | |
| Eigenverbrauch | 0,02W | 3,7W |
| Anschlüsse | Raspberr Pi Connector | LAN, 4x USB-Host, Audio |
| Spannungsmessung, Strommessung, Schraubklemmen | ||
| Verwendete Pins |
3,3V, 5V, I2C1_SDA, I2C1_SCL |
|
| Abmessungen (LxBxH) | 108x90x55mm | 108x90x55mm |